Library: Foundation
Package: Streams
Header: Poco/BinaryWriter.h
Description
This class writes basic types (and std::vectors of these) in binary form into an output stream. It provides an inserter-based interface similar to ostream. The writer also supports automatic conversion from big-endian (network byte order) to little-endian and vice-versa. Use a BinaryReader to read from a stream created by a BinaryWriter. Be careful when exchanging data between systems with different data type sizes (e.g., 32-bit and 64-bit architectures), as the sizes of some of the basic types may be different. For example, writing a long integer on a 64-bit system and reading it on a 32-bit system may yield an incorrent result. Use fixed-size types (Int32, Int64, etc.) in such a case.
Inheritance
Known Derived Classes: BasicMemoryBinaryWriter
Member Summary
Member Functions: bad, byteOrder, fail, flush, good, operator <<, stream, write7BitEncoded, writeBOM, writeCString, writeRaw
Enumerations
StreamByteOrder
the host's native byte-order
big-endian (network) byte-order
big-endian (network) byte-order
little-endian byte-order
Constructors
BinaryWriter
BinaryWriter(
std::ostream & ostr,
StreamByteOrder byteOrder = NATIVE_BYTE_ORDER
);
Creates the BinaryWriter.
BinaryWriter
BinaryWriter(
std::ostream & ostr,
TextEncoding & encoding,
StreamByteOrder byteOrder = NATIVE_BYTE_ORDER
);
Creates the BinaryWriter using the given TextEncoding.
Strings will be converted from the currently set global encoding (see Poco::TextEncoding::global()) to the specified encoding.
Destructor
~BinaryWriter
~BinaryWriter();
Destroys the BinaryWriter.
Member Functions
bad 
bool bad();
Returns _ostr.bad();
byteOrder 
StreamByteOrder byteOrder() const;
Returns the byte ordering used by the writer, which is either BIG_ENDIAN_BYTE_ORDER or LITTLE_ENDIAN_BYTE_ORDER.
fail 
bool fail();
Returns _ostr.fail();
flush
void flush();
Flushes the underlying stream.
good 
bool good();
Returns _ostr.good();
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
bool value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
char value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
unsigned char value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
signed char value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
short value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
unsigned short value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
int value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
unsigned int value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
long value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
unsigned long value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
float value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
double value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
long long value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
unsigned long long value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
const std::string & value
);
operator <<
BinaryWriter & operator << (
const char * value
);
operator << 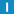
template < typename T > BinaryWriter & operator << (
const std::vector < T > & value
);
stream 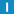
std::ostream & stream() const;
Returns the underlying stream.
write7BitEncoded
void write7BitEncoded(
UInt32 value
);
Writes a 32-bit unsigned integer in a compressed format. The value is written out seven bits at a time, starting with the seven least-significant bits. The high bit of a byte indicates whether there are more bytes to be written after this one. If value will fit in seven bits, it takes only one byte of space. If value will not fit in seven bits, the high bit is set on the first byte and written out. value is then shifted by seven bits and the next byte is written. This process is repeated until the entire integer has been written.
write7BitEncoded
void write7BitEncoded(
UInt64 value
);
Writes a 64-bit unsigned integer in a compressed format. The value written out seven bits at a time, starting with the seven least-significant bits. The high bit of a byte indicates whether there are more bytes to be written after this one. If value will fit in seven bits, it takes only one byte of space. If value will not fit in seven bits, the high bit is set on the first byte and written out. value is then shifted by seven bits and the next byte is written. This process is repeated until the entire integer has been written.
writeBOM
void writeBOM();
Writes a byte-order mark to the stream. A byte order mark is a 16-bit integer with a value of 0xFEFF, written in host byte-order. A BinaryReader uses the byte-order mark to determine the byte-order of the stream.
writeCString
void writeCString(
const char * cString,
std::streamsize maxLength = DEFAULT_MAX_CSTR_LENGTH
);
Writes zero-terminated C-string.
writeRaw
void writeRaw(
const std::string & rawData
);
Writes the string as-is to the stream.
writeRaw
void writeRaw(
const char * buffer,
std::streamsize length
);
Writes length raw bytes from the given buffer to the stream.
Variables
1024 } 
static const std::streamsize DEFAULT_MAX_CSTR_LENGTH { 1024 };